Have you ever mixed up a noun's gender in a language you were learning? That can be awkward and lead to misunderstandings or, at least, awkward situations. What doesn't seem like a big deal to language learners can have an entirely different meaning and make no sense to native speakers. For example, "Les fleurs sont dans le vase" translates from French as "The flowers are in the vase." However, if we're unsure about the gender and say, "Les fleurs sont dans la vase," we say that the flowers are in the mud. So, each version paints a somewhat different picture, doesn't it?
Why do nouns have a gender in the first place? Why do we need to know the gender of objects, for instance? How does one master grammatical gender to avoid miscommunication? Read on to find the answers to these and more questions related to learning languages.
What Is Grammatical Gender?
Grammatical gender is a way to classify some nouns into masculine, feminine, and sometimes neuter. It's important to distinguish between grammatical, lexical, and biological gender. The last two are similar concepts, referring to the natural distinction between genders. That is obvious in words such as "man" and "woman," "hen" and "rooster," which carry associations with biological gender. Grammatical gender, on the other hand, is different from the lexical or biological gender.
Unlike biological gender, the one in a language doesn't usually have much in common with the object and its features. For instance, in Italian, you say "la luna è bella" to express that "the moon is beautiful." Note how the adjective changes for a masculine noun in "Il cielo è bello," translated as "The sky is beautiful." The only way to learn the gender of these nouns is to learn it.
Learning a grammatical language is considered more challenging. To English speakers, it is strange to think about the gender of nouns like "heart," "potato," or "cabbage." That adds to the learning curve when learning Romance languages (French, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese), Germanic, Slavic, and languages like Greek, Arabic, and others. Many languages have lost their grammatical gender systems as they evolved. Examples include English, Hungarian, Finnish, Turkish, and many East Asian languages.
Why do we need to learn the grammatical gender of nouns? Won't native speakers get our message despite a few minor mistakes? They might. However, as mentioned above, sometimes, changing the gender may also change the word's meaning. On top of that, getting noun genders right contributes to your fluency.
Where Does Grammatical Gender Come From?
Linguists trace the origins of grammatical gender back to the Proto-Indo-European family. It is the ancestor of many modern languages. The original system is thought to have divided nouns into living or animate and non-living or inanimate. That classification was the foundation of more complex gender systems over time. In other words, by changing forms to agree with the gender of the noun, the goal of a grammatical gender was to eliminate ambiguity. As a result, it's clear what the speaker is referring to in a conversation.
Grammatical gender evolved, and some languages even lost it altogether. English is one language that no longer has grammatical gender for inanimate objects. The change occurred in the 11th century under the influence of Old Norse. The Viking raids and settlements started in northern England and spread southward. Toward the end of the 14th century, London English no longer had a grammatical gender. The change was part of a more significant process, during which Old English grammar was simplified to make communication easier with Old Norse speakers.
Which Languages Use Grammatical Gender?

Around half of the world's languages distinguish between two or three grammatical genders. According to a study, grammatical language influences the way speakers describe objects. For instance, in German, "key" is masculine ("der Schlüssel"), so it's often described as "heavy" by German speakers. The same word is feminine ("la chiave") in Italian, so it's often described as "beautiful." That's something worth paying attention to when learning a foreign language. As an effect, you become more fluent.
Many languages around the world use grammatical gender systems. Most categorize nouns into at least two groups - feminine and masculine. Some examples are listed below:
Romance languages: French, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, Romanian.
Germanic languages: German, Dutch, Icelandic, Swedish.
Slavic languages: Russian, Polish, Czech, Slovak, Ukrainian.
Other Indo-European languages: Greek, Sanskrit, Latin.
Afro-Asiatic languages: Arabic, Hebrew, and Hausa.
Nakh-Daghestanian languages: Chechen.
Bantu languages use noun classes, which may be considered a form of grammatical gender.
Languages that don't have a grammatical gender include English, Afrikaans, Turkish, Finnish, Hungarian, and Estonian. Many Asian languages, such as Chinese, Japanese, and Korean, also do not have a grammatical gender.
How to Master Grammatical Gender
Grammatical gender is rarely assigned arbitrarily. At the same time, it doesn't follow an entirely predictable pattern. For that reason, memorizing noun gender can seem challenging, especially to beginners.
To better learn lexical gender, try the following tips:
- Memorize nouns together with the articles. For instance, learn the German "die Katze," not only "Katze," and the Spanish "la casa" instead of just "casa."
- Use informative flashcards. Associate the word with the article or an image.
- Memorize an example of a sentence together with the word. When you need to make another sentence with the same word, you only need to replace the rest of the words.
- Learn some rules in the gender system. For example, nouns ending in -o are masculine in Spanish, and the ones ending in -ung are feminine in German. While there are exceptions, these patterns can help make sense of lexical gender.
- Group nouns by gender. Exercise as often as possible and pay more attention to the nouns you get wrong.
- Learn nouns with adjectives. Aim for words that frequently go together in the target language. For French, repeating "un bon vin" (a good wine) clarifies that the noun is masculine. On top of that, you have a phrase ready to use the next time you're at a French restaurant.
- Prioritize high-frequency words. One mistake beginners make is learning long lists of words. Start with the most used words, phrases, and expressions to optimize learning.
This will give you the most practical benefit in everyday communication and make it easier to understand spoken and written texts.
With time, linguistic gender becomes second nature. In some cases, you can correctly determine it for new words. In all other cases, you will deduce grammatical gender from context.
Learn Grammatical Gender Intuitively with FunEasyLearn
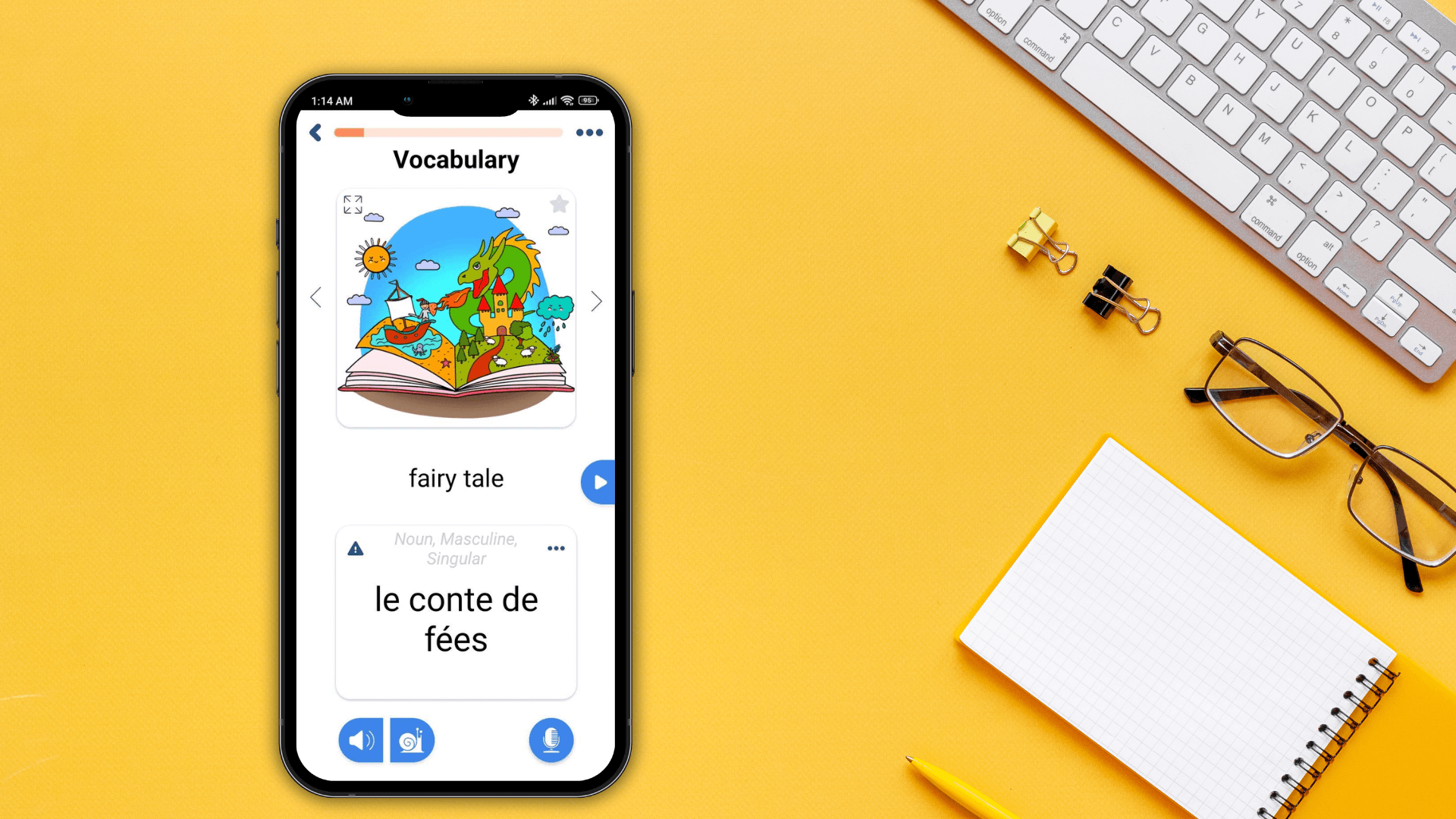
Mastering grammatical gender is a crucial step in becoming fluent in many languages, and with FunEasyLearn, it's easier than ever.
Out of the 32 available language courses, 23 include gendered languages, namely :
| Arabic | Croatian | Greek |
| Bulgarian | Czech | Hebrew |
| Catalan | Danish | Hindi |
| Dutch | French | Italian |
| German | Norwegian (Bokmål) | Polish |
| Portuguese (Portugal) | Portuguese (Brazil) | Romanian |
| Russian | Slovak | Spanish |
| Swedish | Ukrainian |
There are many benefits to mastering the lexical gender of a new language. First of all, you communicate more confidently with native speakers. Your accuracy and fluency improve significantly. Secondly, you gain a better understanding of the language as a system. The reason is that you focus on the message instead of thinking about whether you used the correct article, adjective, or verb form.
🗂️Informative Flashcards
Engage with vibrant, informative flashcards that make learning a visual delight. Each card is designed to help your brain quickly learn new words while minimizing effort. They're ideal for visual learners and analytical thinkers.
🎮 30+ Fun Learning Games
Repetition is key to learning. Enjoy a wide range of interactive games incorporating the new words in context, keeping your learning journey fun and engaging.
♻️ Smart Review System (Premium)
Focus on the most challenging words with a review system that calculates the best time to practice certain vocabulary. Review the words until you commit them to your long-term memory. That way, you ensure a solid understanding of grammatical gender.
Summing Up
Grammatical gender has the role of clarifying what exactly the speaker is referring to. Some languages have lost their grammatical gender during their evolution. Other grammatical systems classify nouns into a minimum of two genders: masculine and feminine. Many languages also have a neutral gender. Some have even more gender classifications. Learning the gender of the nouns improves fluency and understanding of the target language.
The language learning app FunEasyLearn makes it easy to learn grammatical gender through fun, educational games.
Are you ready to master a new language?